This time, we introduce a research paper reporting that NMN suppresses reproductive dysfunction induced by BBP (benzyl butyl phthalate), a type of phthalate ester.
BBP is a chemical substance used in various products in modern society. BBP is thought to have toxic effects on living organisms, one of which is reproductive dysfunction. However, NMN treatment may offer a potential way to avoid reproductive dysfunction caused by BBP.
Who should read this column?
✅ Those who want to know how BBP intake affects pregnancy risks
✅ Those who are planning to conceive in the future
✅ Those who want to minimize risks to their children during pregnancy
✅ Those who want to keep their oocytes healthy
What is BBP?
**BBP** is a type of phthalate ester and is designated as a Class I specified chemical substance (Ordinance No. 273) under the government’s environmental policy. It is used as a plasticizer in products like floor tiles, conveyor belts in factories, synthetic leather, and indoor decorative items. While various toxicities have been reported in animal experiments with BBP exposure, human data is limited, and the toxicity remains unclear. However, the European Chemical Bureau (ECB) classifies BBP as a **toxic substance**. Moreover, phthalate esters in general are suspected to have endocrine-disrupting, reproductive toxic, and carcinogenic effects on humans, leading to some regulations on their use domestically and internationally.
For example, in Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare issued Notification No. 267 in August 2002, stating that “PVC-based synthetic resins using two types of phthalate esters (DEHP, DINP) as raw materials must not be used as toy raw materials.” Additionally, in the same year, the use of DEHP in PVC-based synthetic resins for utensils/containers packaging in contact with oil and fatty foods was generally prohibited.
Furthermore, under the EU REACH regulation, as of July 7, 2020, the marketing of molded products containing a total of 0.1% or more by weight of four phthalate esters (DEHP, DBP, BBP, DIBP) is restricted.
Potential Health Effects of Exposure to Phthalate Esters
– Decrease in testosterone (male hormone) levels
– Reduced reproductive ability in women and men
– Potential cognitive or behavioral disorders in babies
– Changes in endocrine function and thyroid hormone function
– Toxicity to kidneys and liver
– Association with certain types of cancer
– Type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, allergies, asthma

BBP is Ubiquitous in Daily Life
BBP is widely used in the manufacture of PVC flooring, waterproof sheets for tablecloths, synthetic leather for sofas and coats, vinyl gloves, and adhesives. Trace amounts of BBP have also been detected in various foods, especially fish products, due to its tendency to concentrate in aquatic organisms. BBP has also been detected in air, drinking water, and house dust. Moreover, BBP can be released into the environment during the manufacturing and disposal processes of BBP-containing products. Exposure to BBP is said to potentially harm human health, but direct evidence of its effects on human reproductive function is still lacking.
The paper we are introducing investigates the reproductive toxicity induced by BBP in female mice and how NMN acts against it.
Experimental Details
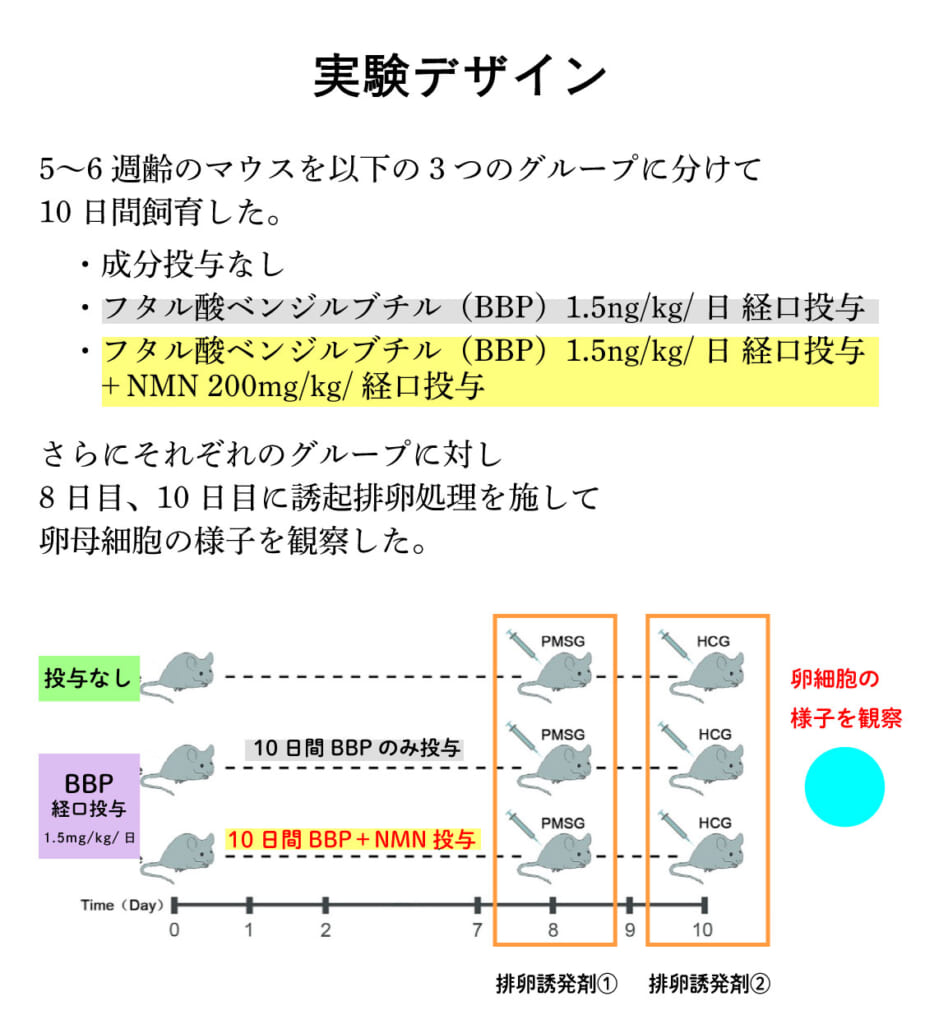
Female mice aged 5-6 weeks were divided into three groups and reared for 10 days. Each group received ovulation-inducing hormones on the 8th and 10th days to promote superovulation, after which the condition of the oocytes was observed to investigate the effects of NMN administration.
① Female mice without BBP/NMN administration
② Female mice receiving intraperitoneal BBP (1.5 mg/kg/day)
③ Female mice receiving intraperitoneal BBP (1.5 mg/kg/day) + NMN (200 mg/kg/day)
*NMN is administered intraperitoneally
*1: phosphate buffered saline, a reagent that has a buffering capacity to prevent pH fluctuations when dissolving chemical substances, which might otherwise lead to strong acids or bases.
After promoting superovulation with ovulation-inducing hormones on the 8th and 10th days, the oocytes were observed to study the effects of NMN administration in aged mice.
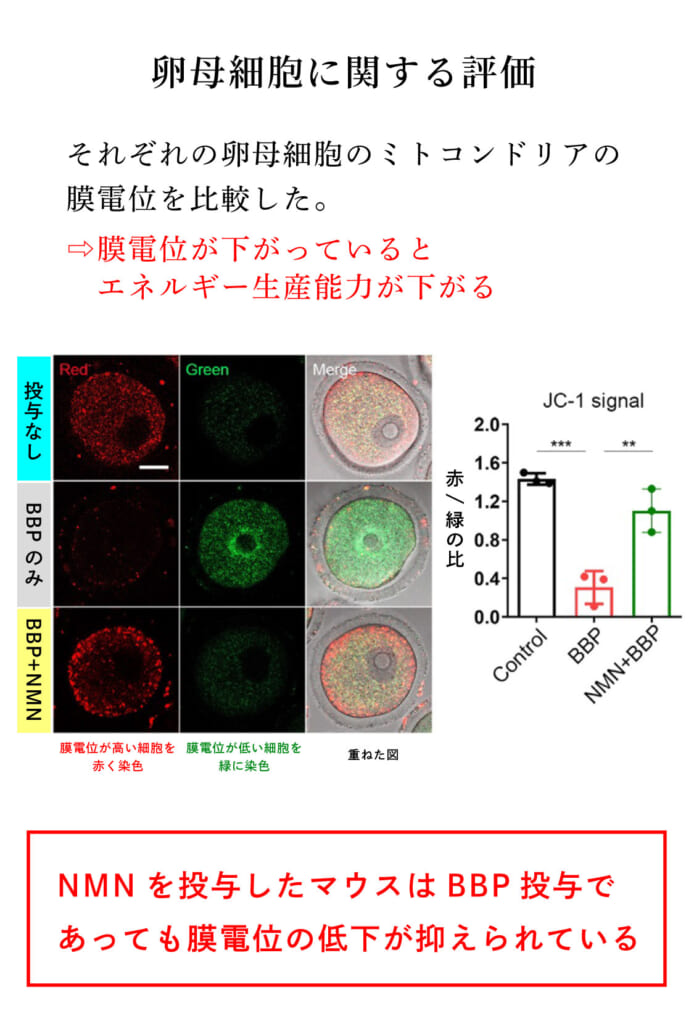
Evaluation of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential in Oocytes
Mitochondrial membrane potential was assessed using JC-1 staining, which promotes ATP synthesis in mitochondria. High membrane potential mitochondria show red signals, while low membrane potential mitochondria show green signals. Oocytes from female mice exposed to BBP showed more green signals, but female mice administered NMN had a suppressed decrease in membrane potential, comparable to female mice not exposed to BBP.
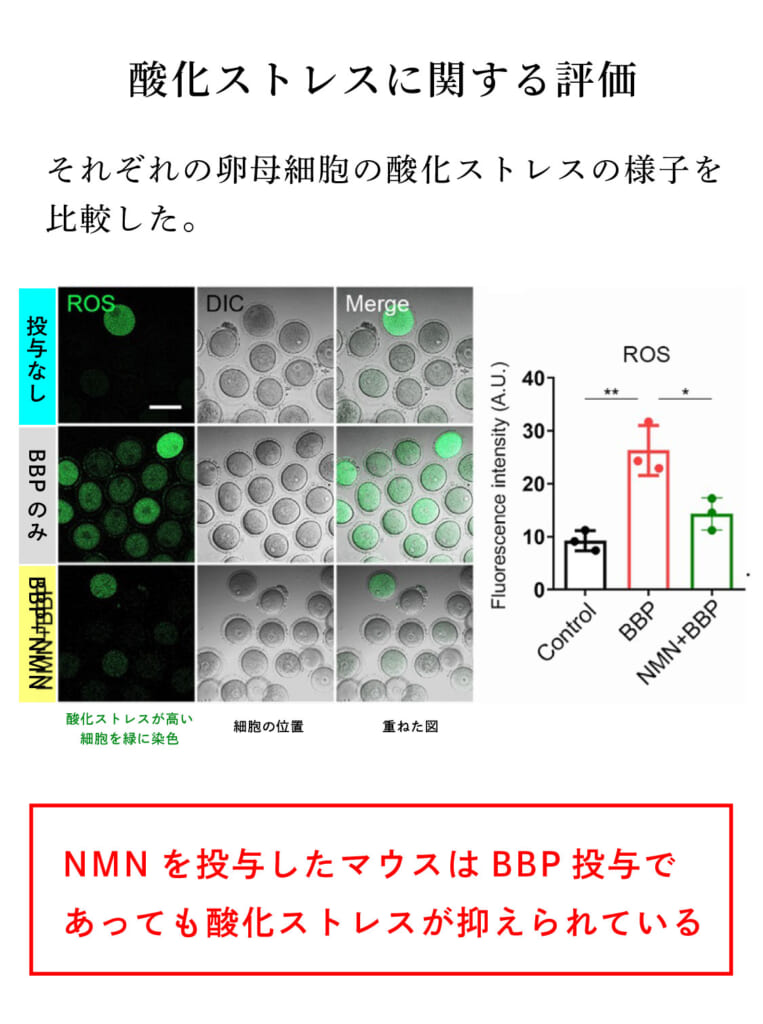
Evaluation of Oxidative Stress
The main cause of mitochondrial dysfunction is the accumulation of ROS (reactive oxygen species) and oxidative stress. The ROS levels in oocytes from each group were compared using dichlorofluorescein (DCFH) staining.
The results showed that oocytes from BBP female mice were stained green, indicating high ROS levels, but NMN-administered female mice showed ROS levels comparable to those of unexposed female mice. This indicates that oxidative stress was suppressed by NMN.
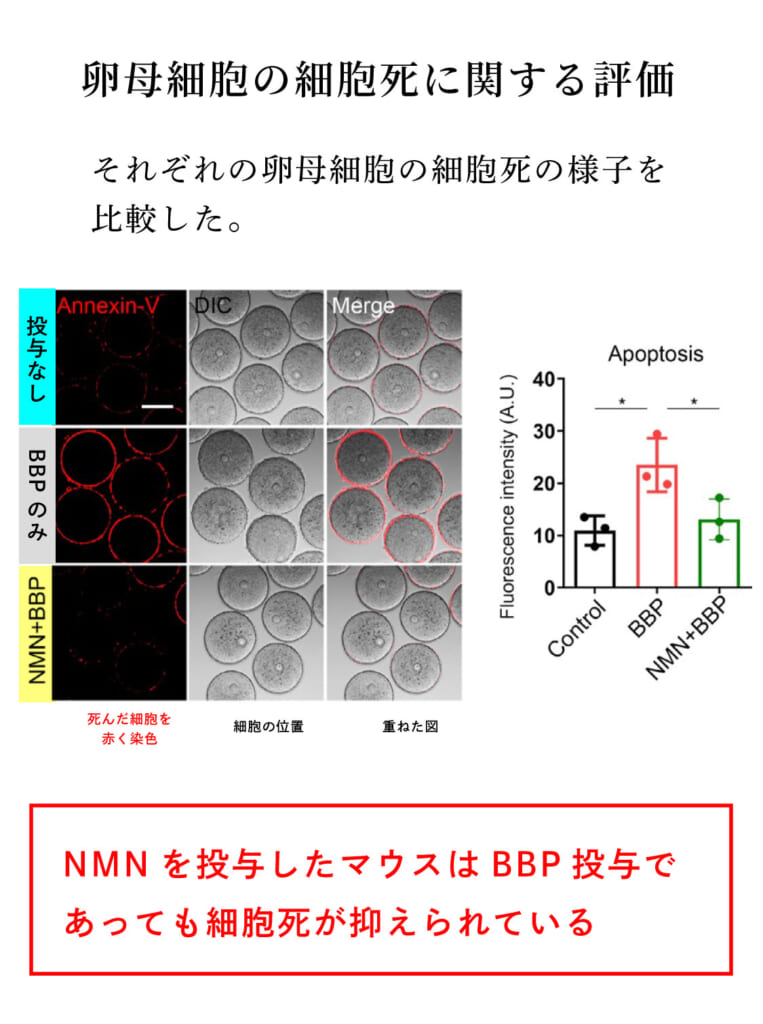
Evaluation of Apoptosis in Oocytes
Excess ROS can lead to DNA damage accumulation and induce early apoptosis (cell death). DNA damage and early apoptosis levels in oocytes from each group were examined using γ-H2A.X staining and Annexin V staining.
Apoptotic cells were stained red, and apoptosis was prominent in BBP female mice. However, NMN-administered female mice showed suppressed apoptosis despite BBP administration. This suggests that exposure to BBP induces early apoptosis and negatively impacts oocytes, but NMN administration effectively mitigated these adverse effects.
*Graphs and photos are adapted from the original paper.

NMN May Reduce the Risks of BBP
These experimental results suggest the mechanisms of BBP-induced reproductive toxicity in females and the potential therapeutic effects of NMN in reducing these toxic risks. BBP is used in various products, especially in soft plastics like PVC, and is often listed simply as “fragrance” in products like perfumes and hair sprays.
Although the toxicity of BBP to human health is not yet clear and there is no need to be overly sensitive, reproductive effects have been demonstrated in animal experiments. Given the observed negative effects on offspring, it is wise for pregnant women or those wishing to conceive to avoid BBP as much as possible.
However, as BBP is prevalent in our daily lives and cannot be completely avoided, it might be beneficial to consider using NMN supplements. They may help prevent the risk of reproductive function decline due to BBP and keep oocytes healthy.
References
Reference Paper: [Nicotinamide mononucleotide restores oxidative stress-related apoptosis of oocyte exposed to benzyl butyl phthalate in mice]
Journal Name/Volume: Cell Prolif. 2023 Aug;56(8)
You can access the paper here (PubMed)
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36756972/
